Ways of expressing concentrations 2
Table of Contents

Normality
The fourth method in ways of expressing concentrations of solutions is
Normality is defined as the number of gram-equivalents of solute present per liter of solution.
The units of normality are gm-equivalent per liter
It is commonly expressed as N

Mathematical Expression
The number of gram equivalents can be calculated by the following formula.
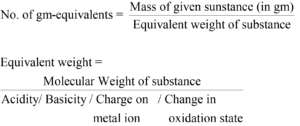
Acidity:
Acidity is expressed for a base, and it is the number of moles of hydronium ion required for complete neutralization of the base.
Basicity:
Basicity is expressed for an acid, and it is the number of moles of hydroxide required for the complete neutralization of acid.
Charge on metal ion:
For calculating the equivalent weight of the salt (electrolyte) this method is used. The total charge on metal ions is used to calculate their equivalent weight.
Change in oxidation state:
In the redox equation change in oxidation state is used for calculating the equivalent weight.
Calculate normality of Sulphuric acid solution when 1.96 gm of sulphuric acid is dissolved in water to form 750 mL of solution?
Answer:
Weight of solute = 1.96 gm
Volume of solution = 750 mL

Molarity
The fifth method in ways of expressing concentrations of solutions
it is expressed by M (molar). It is defined as the number of moles of solute present per litre of solution or the number of moles of solute with respect to the given volume of solution in litres.
The units of molarity are moles per litre or moles per cubic centimetre.
It is the most common method of expressing the concentration of the solution in chemistry.
Mathematically molarity is expressed as

Mathematical Expression
Calculate the molarity of aqueous hydrochloric acid solution when 1.825 gm of HCl is dissolved in water to form 1500 mL of solution.
Answer:
Wt. of Solute (HCl) = 1.825 gm
Volume of Solution = 1500 mL

Molality
The sixth method in ways of expressing concentrations of solutions
It is expressed by m (molal). It is defined as the number of moles of solute present per kilograms of solvent or the number of moles of solute with respect to the weight of solvent in kilograms.
The units of molality are moles per kg.
Mathematically molality is expressed as

Mathematical Expression
Calculate the molality of the aqueous sugar syrup solution when 6.84 gm of sugar (sucrose) is dissolved in 500 gm of water to form a solution.
Answer:
Wt. of Sugar= 6.84 gm
Molecular wt. of sugar =342 gm/mol
Wt. of water =500 gm
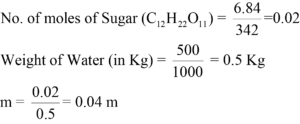
Mole Fraction
The seventh method is ways of expressing concentrations of solutions
It is expressed by X. It is the ratio of moles of a component with respect to the total number of moles of all the components present in the solution.
For a binary solution, A and B the mole fraction of A can be expressed as the number of moles of A with respect to the total number of moles of A and B.
For a binary solution, the algebraic sum of the mole fraction of A and the mole fraction of B would always be unity and this holds true for any solution.
Mathematically mole fraction can be expressed as

Mathematical Expression
Calculate the mole fraction of sodium chloride in an aqueous solution, when 3.51 gm of sodium chloride is dissolved in 100 gm of water.
Answer:
Wt. of NaCl = 3.51 gm
Molecular wt. of NaCl= 58.5 gm/mole
Wt of water = 100 gm
Molecular wt. of water = 18 gm/mole

Parts per million (ppm)
This is the eighth way of expressing the concentration of the solution.
This is preferred only when the solute is present in trace quantities for example the amount of Sulphur dioxide in the air. Amount of pollutants present in water.
The parts per million can be expressed as mass to mass or volume to volume or mass to volume. When expressing the amount of chlorine as a disinfectant present in the water the mass-to-volume relationship is used.
When expressing the volume of Sulphur dioxide as a pollutant present in the air is expressed in volume to volume relationship.
It is defined as the volume or mass of a component with respect to the total number of parts of all the components of the solution. Mathematically it can be expressed as

Mathematical expression
6 milligrams of Oxygen are dissolved in 1030 gm of seawater. Express the concentration of in ppm?
Answer:
Weight of oxygen = 6 mg
Weight of seawater = 1030 gm
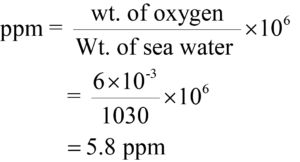
You may like
Become a Member
Purchase a membership for expert guidance tailored for IIT, NEET, and CBSE exams. Unlock your potential and ace your exams with personalized tutoring and resources!
Purchase YouTube channel
Watch Our content tailored to help you excel in JEE Mains and NEET-UG. With expert tips, educational videos, and insights, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge and strategies you need to succeed in your exams
Join Channel Telegram Chanel
Join our Telegram channel to unlock a treasure trove of practice papers tailored for IIT, NEET, and CBSE exams. Stay ahead of the curve and ace your tests with confidence!
Join Channel 